

OLAP servers are commonly used in data mining and data warehousing operations. Used to guide future plans and strategies. Monitors and records ongoing business transactions, such as purchases and sales.įinds patterns that can help explain issues. Other differences between the two are highlighted in the chart below: While OLTP handles the processing of data created in a business’s typical day-to-day operations, OLAP seeks to identify trends and help companies better prepare for the future. OLAP is frequently compared to OLTP, or online transactional processing. Let’s take a closer look now at what distinguishes OLAP from operational analytics. This is opposed to operational analytics, or analytics aimed at processing data used in the business’s operations in real time or near real time. In most contexts, a human user guides the analysis. Generally, OLAP tools are used for historical analysis aimed at deriving insights about trends affecting the business, problems, opportunities for growth etc. For instance, to understand why total sales plummeted in a given quarter, it may be necessary to drill down to a more detailed level: sales by store, and then compare that category with data on the types of products sold. You may have noticed that these dimensions can generally be grouped into conceptual hierarchies, and OLAP allows analysts to easily navigate between levels in these hierarchies to understand business problems. Dimensions of data include geographic categories (country, city, state), temporal categories (year, month, day), levels of aggregation (total sales, sales by store, sales by dept), etc. Both end-to-end BI platforms and modern, self-service BI tools offer traditional OLAP or equivalent capabilities for multidimensional analysis.Īs we’ve already suggested, the primary characteristic of OLAP is that it’s multidimensional. It’s important that companies shopping for business intelligence (BI) tools be familiar with OLAP. The power of OLAP is its ability to identify and anticipate trends-goals which are central to most business intelligence initiatives.
#LIST OF BI TOOLS SOFTWARE#
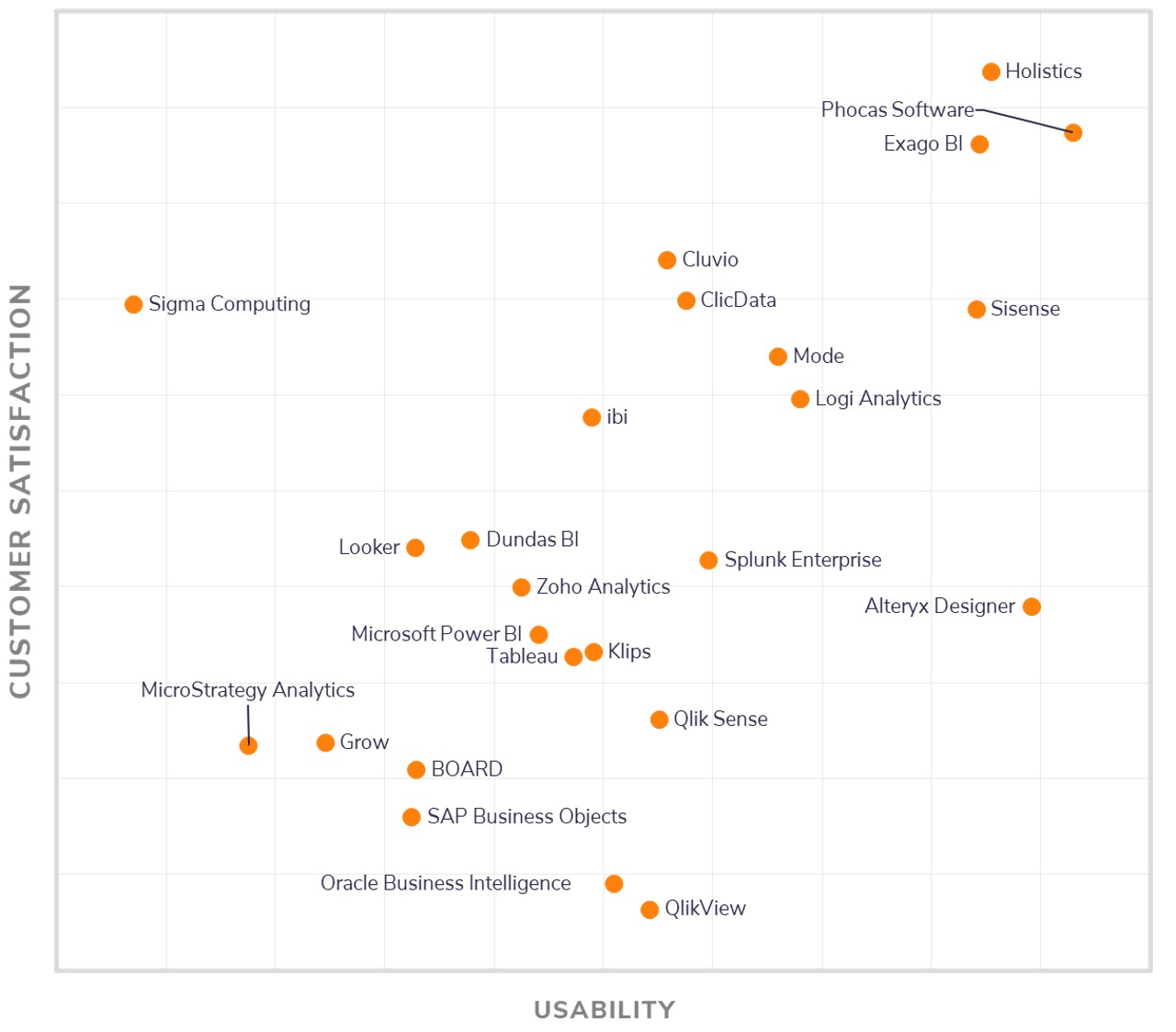
Note: The best self-service BI tools are listed in alphabetical order.Online analytical processing, or OLAP, is a software capability used to create actionable business intelligence from a company’s available data by empowering analysts to navigate hierarchical relationships between categories and levels of detail in the data (known as dimensions).

We’ve also included platform and product line names and introductory software tutorials straight from the source so you can see each solution in action. To make your search a little easier, we’ve profiled the best self-service BI tools providers all in one place. Choosing the right vendor and solution can be a complicated process - one that requires in-depth research and often comes down to more than just the solution and its technical capabilities. The editors at Solutions Review have developed this resource to assist buyers in search of the best self-service BI tools to fit the needs of their organization.
#LIST OF BI TOOLS FREE#
Information was gathered via online materials and reports, conversations with vendor representatives, and examinations of product demonstrations and free trials. Solutions Review’s listing of the best self-service BI tools is an annual sneak peek of the top tools included in our Buyer’s Guide for Business Intelligence Platforms and companion Buyer’s Matrix Report.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
